

'The Aral Sea (1977-2008) NASA Landsat Images Archive (Click to View Image Source) |
Environmental Health Crisis
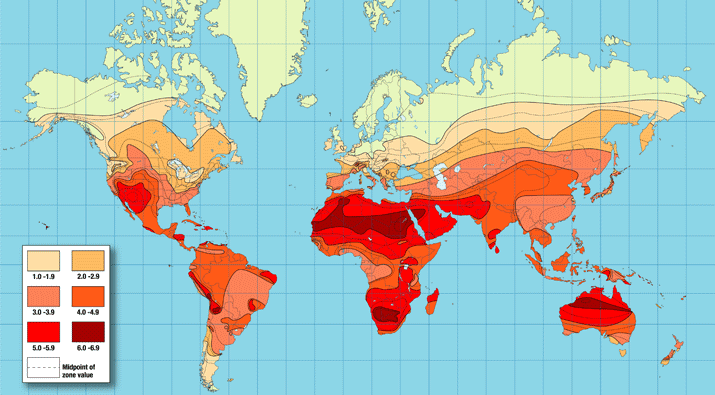
Water has been identified as a central challenge for humanity in the coming decades. Diseases related to water and air pollution consistently rank in the top ten causes of death globally 1. Combined, water, air, and soil pollution are estimated to cause 40% of all deaths worldwide 2. Beyond humans, the overuse, contamination, and widespread destruction of natural water bodies and wetlands has seriously impacted the health of many other species 3. Climate change is anticipated to further exacerbate the water crisis, habitat loss, and the infectious disease load in the coming decades 4. Resource scarcity, disease, and environmental pollution are exacerbated by a lack of local environmental data, public awareness of global and local environmental conditions, and public access to and acceptance of appropriate sustainable technologies and lifestyle choices.
Water Crisis
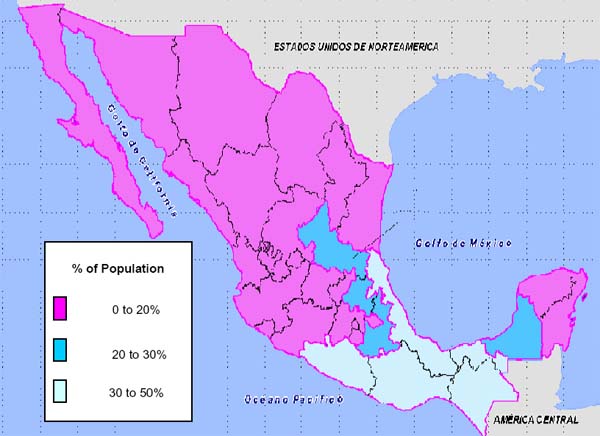
Water scarcity and pollution has been critical concern for global public health efforts for decades. Although ~1/6 of the global population still lacks access to safe water sources, water infrastructure development projects have made significant headway 6. Efforts to acquire more fresh water include drilling more and deeper wells and constructing more extensive water distribution networks and aqueducts. As a result the consumption rates of ground water have more than doubled since the 1950’s (Wada 2010, ).
| "When the well's dry, we know the worth of water." | |

|
Benjamin Franklin, (1706-1790), Poor Richard's Almanac. |
|
|
|
|
Scarcity, Extraction, Depletion Dynamics
Global aquifer depletion rates indicate that the strategy of addressing water demand and scarcity with more, deeper, and larger volume wells has become self-limiting thus more sustainable means of reducing water usage and increasing water supply must be developed. This dilemma in which the socio-economic strategy of responding to scarce resources by intensifying extraction efforts leads to greater scarcity is known as "The Tragedy of the Commons" or the Scarcity Extraction, Depletion Dynamic and is related to the "Law of Diminishing Returns" in economics. Unfortunately, the Tragedy of the Commons or SED dynamics are not unique to fresh water; other important examples of it occur in the management of energy, agricultural, and wildlife resources (see the SED interactive below).
Select Example:
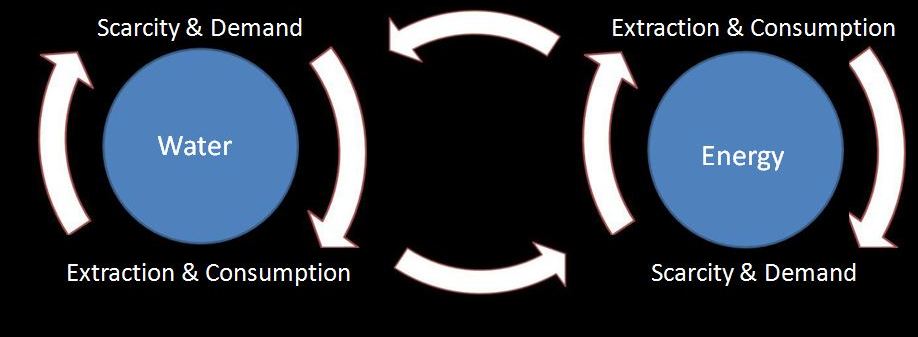
The Water Energy Nexus
Water extraction and consumption requires energy for drilling, pumping, processing, and distribution. Thus deeper wells, lower water levels, and increasingly contaminated water supplies imply greater energy consumption in pumping and purifying ground water.
The water energy connection also operates in the other direction. Water extraction and processing requires energy inputs but water is also integral to the production of electrical energy. The extraction and consumption of fossil, nuclear, and biomass based fuels from bare rock and dry soils requires water for quarrying and processing. Hydraulic mining and fracturing (fracking) are rely on intensive water usage. Thermoelectric generation from these fuels sources also requires water for cooling of plant equipment. Electrical power is a major source of water withdrawals in the US and world wide. In 2005 Thermo-electric power water withdrawals accounted for 53% of the freshwater withdrawals.20
(Use the options to the lower left to investigate each leg of the cycle)
|
How energy use, uses water?
How water use, uses energy? |
|
The Water Energy Climate Nexus
|
“When one tugs at a single thing in nature, he finds it attached to the rest of the world."
Attributed: John Muir (1838-1914) |

|

|
Population and food
Agriculture consumes… water and energy These sectors explain how % humans w/o water yet water extraction per capita is rising at a faster pace than the population itself Climate Change- driven by the water, food, and energy production/consumption and in turn driving global ecological changes which will impact all of these sectors both directly and indirectly. Wildlife will also pay the price

|
References:
1. Water Scarcity a Looming Crisis? Alex Kirby, BBC News. 10/19/04
2. Water, Sanitation, and Hygiene Links to Health. World Health Organization. 2005.
2E. Spanish version: Water, Sanitation, and Hygiene Links to Health. World Health Organization. 2004.
3. Costs and benefits of water and sanitation improvements at the global level. Water Sanitation and Health; world Health Organization. 2004.
energy/water Use EW_roadmap some
and
ETIP-DP-2010
Water Resources and the Scarcity, Extraction, Depletion Cycle
http://www.sandia.gov/energy-water/nexus_overview.htm
oil http://www.beg.utexas.edu/UTopia/images/pagesizemaps/oilgas.pdf
and
land subsidence:
http://ga.water.usgs.gov/edu/earthgwlandsubside.html
http://www.unep.or.jp/ietc/publications/short_series/lakereservoirs-2/9.asp
http://www.nap.edu/openbook.php?record_id=4937&page=16
water depletion
http://ga.water.usgs.gov/edu/gwdepletion.html
http://www.southwestclimatechange.org/figures/aquifer_decline
thermoelectric
http://ga.water.usgs.gov/edu/wupt.html
http://www.wri.org/chart/typical-range-water-withdrawals-and-consumption-thermoelectric-power-plants
Water used in mining and extraction
http://ga.water.usgs.gov/edu/wumi.html
Land subsidence
"As the water table declines, pores in the alluvium once held open by water pressure are no longer supported and collapse. Collapse and subsequent lowering in elevation of the land surface is defined as land subsidence. This subsidence is generally not recoverable. If this subsidence occurs over areas of bedrock, differential subsidence can occur."
http://www.azwater.gov/azdwr/hydrology/geophysics/landsubsidenceinarizona.htm